Gut feeling or data-driven decision? You have a choice!
DDDM – the practice of basing decisions on data
Big Data, Advanced Analytics, Business Intelligence – these are all terms that are covered under the umbrella of Data-Driven Decision Making. This is the practice of rigorously collecting data, analysing it, and basing decisions on insights derived from the information.
Data-Driven Decision Making (DDDM) is an objective approach that, if you do it right, can easily be evaluated according to the impact on your defined metrics. DDDM becomes more sophisticated when used for Predictive Analysis, the use of historical data to predict the future. However, many companies still base their decision–making on gut feeling, theory, tradition or instinct.
Data–Driven Decision Making is heavily quantitative. It requires powerful computer systems to continuously collect and analyse large data sets (Big Data). This used to be only for the few, but today prices are moderate, and Cloud Services are available to basically everyone.
While the ability to do large scale number crunching is there, the success of Data–Driven Decision Making depends on the quality of the data you have collected and the methodology you use to analyse it.
Why should you apply DDDM?
72% of businesses are collecting data that they will never be able to use (Corporate Renaissance Group). Data quality and focus is essential to data leadership in decision-making processes: you need not collect as much data as possible, but the right data fit for your purpose.
With a well-structured DDDM approach, your company will be able to monitor results in near real time, detect early warnings and be able to become even more customer-focused and competitive. You will be able to detect new business opportunities much faster, become more agile and respond to the market change much more quickly.
Data–Driven Decision Making creates greater transparency in terms of concrete business goals and measurement. With greater transparency comes a greater sense of control. 91.7% of businesses state that their DDDM initiatives have started due to transformation, agility or competition drivers (New Vantage Partners).
How to begin?
Start small, with a pilot in one part of the business.
- Select a business area to focus on
- Define the objectives
- Create the hypothesis
- Identify the data needed
While this may seem fairly easy, our experience proves that already in this part of the process a lot of questions and uncertainties arise:
- Data sources are fragmented, from different systems, entities and geographic clusters
- Metadata, master data and transactional data are not defined or aligned
- Ownership of data and of maintaining information is not defined or anchored
- Processes and standards for quality assurance, compliance, security etc. are not defined or anchored
In Sofigate, we have the Data Leadership Development Journey framework to help our clients mature their approach to data leadership. Having a structured way of implementing data leadership enables thorough analysis of purpose and need on multiple levels.
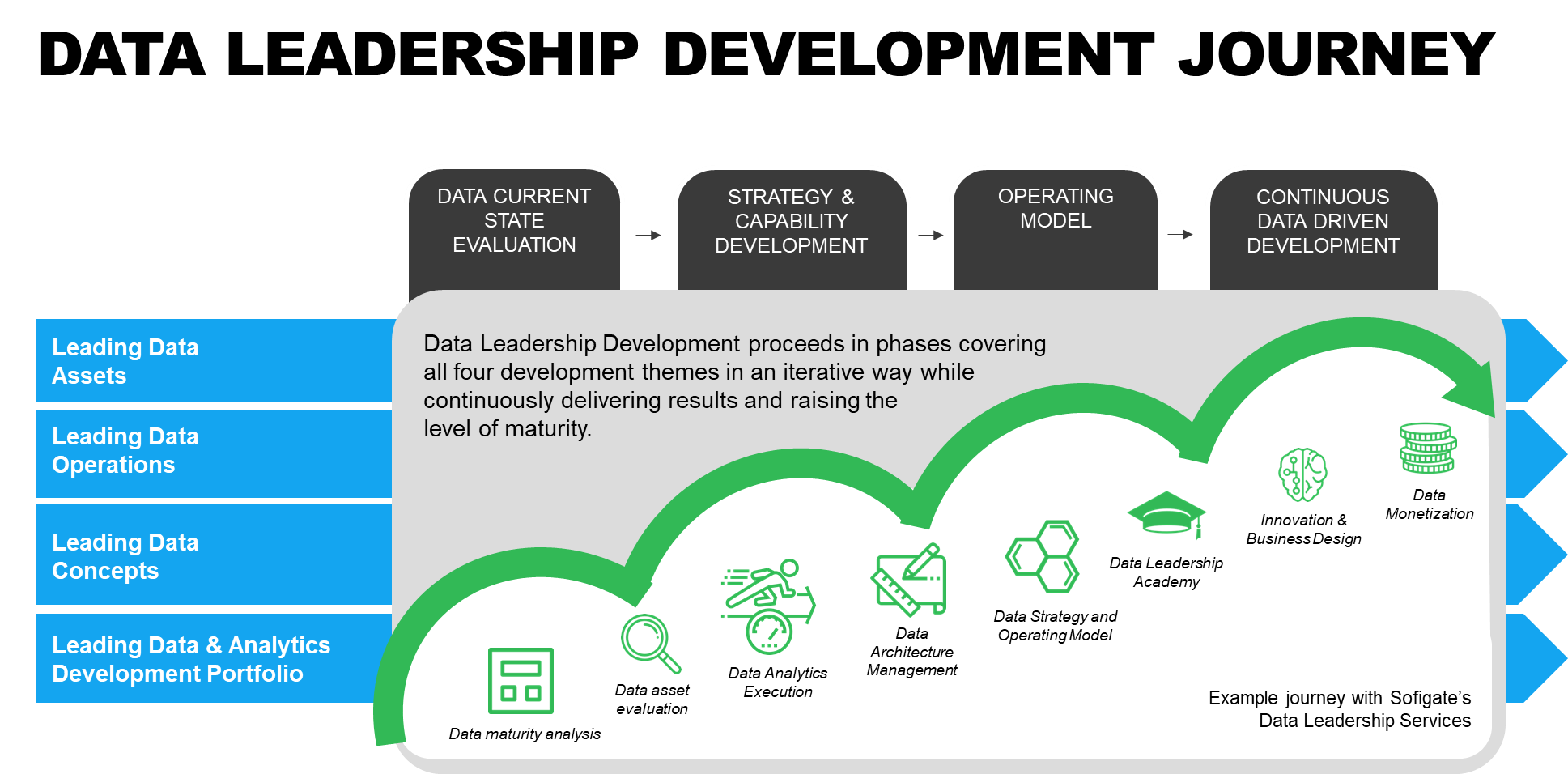
This enables a clear development of data leadership across data assets, operations, concepts and data & analytics development portfolio. Through this the holistic discipline of data management is covered and introduced to the organisation, enabling a data-driven organization that can utilise data to its full potential.
References:
Corporate Renaissance Group, How Data Visualization Leads to Better Decision Making. Online source.
New Vantage Partners. Big Data and AI Executive Survey 2019. Online resource.