How to run successful Enterprise Service Management projects
Companies are beginning to understand the benefits of digital enterprise service management (ESM) tools but struggling with implementation. Based on our experience in implementing hundreds of IT service management projects and dozens of ESM projects, here are some of our key learnings and essential tips on how to run successful ESM projects.
Enterprise service management means applying the principles of IT service management to other areas of an organisation such as HR, finance, facility management and procurement. The goal is to improve performance, efficiency and service delivery.
IT service management (ITSM), first saw light in the late 1980s when the first version of IT infrastructure library (ITIL) best practices was released. In the last 5–10 years, ITSM has expanded to more generic service management, covering other internal enterprise functions that serve the business. While implementing processes and tools for the new service areas we can apply the experience gained from four decades of ITSM.
ESM and ITSM projects are different – learn each other’s languages and prepare for a slower pace
Typically, ESM projects are run by IT people who have earlier been involved in building ITSM practices. However, there are some aspects that are specific to ESM projects. Here are a few things to which project managers, developers and tool owners should pay attention:
- Language. You will need to learn each other’s languages. The HR team don’t necessarily understand ITSM jargon, and the IT team need to learn the essential terms and processes of other business functions to successfully implement ESM processes. For example, “Event Management” in the facilities world means organising events like conferences, while in IT, “Event Management” is the process that monitors all events that occur through the IT infrastructure.
- Project duration. The pace of an ESM project is typically slower than an average IT project. Decision-making may take more time, because the service function team need to agree on target processes or tool requirements with many stakeholders. For example, if you are running a project with the finance department, check their financial cycle milestones. There are days when the finance team are busy with end of month/quarter/year activities and not able to contribute to your project as much.
- Global vs. local. In global companies’ IT, we normally work with global processes. In ESM, it might not always be possible due to differences in local legislation. Talk about this with your ESM team during project planning, as instead of one process, there may in fact be multiple processes – one in each country.
- Processes first! IT people can be eager to rush to technical solutions. However, it’s important to define and agree on processes first. ESM processes, especially those in financial or master data management, can be much more complex than IT processes, and defining them can take a lot of time.
The seven steps of ESM project implementation
Based on our experience in implementing hundreds of ITSM projects and dozens of ESM projects, we recommend the following steps for any ESM project, in this order:
- Start from service portfolio definition. What services are the enterprise functions offering to employees? What kind of requests can employees make? An analysis of existing resource mailboxes can be a good source of information for your list of the most popular requests and questions.
- Decide on prioritization. Which requests should be implemented first? Define their fulfilment processes.
- After finding the most popular questions, analyse and clean up your existing information sources and start turning it into knowledge articles that give the company’s personnel answers to frequently asked questions. Agree on how knowledge management should be handled in the future – who will be responsible for updating information about different topics?
- Start tool implementation. We highly recommend applying service design principles at least for the portal but optimally for the whole service, which includes the portal visible to users, and backend, where support functions fulfil requests and maintain knowledge articles.
- Pay attention to change management. The result of your project can be a big change in the daily life of many people. Communication, user trainings and support clinics should be planned well in advance.
- Don’t stop activities after the first tool deployment – move it to continuous improvement Agree on a process for keeping the service request catalogue and knowledge articles up to date and always identify new requests or missing information.
- After manual requests implementation, analyse what can be automated. Automate where possible.
Follow an iterative approach
When it comes to the implementation, we strongly recommend following an iterative approach. Don’t try to move all functions to a new world in one go as it will be extremely complex technically. Moreover, it will be difficult to manage communication to all impacted people and ensure a successful change.
Here is one example of how to approach service catalogue implementation using iterations:
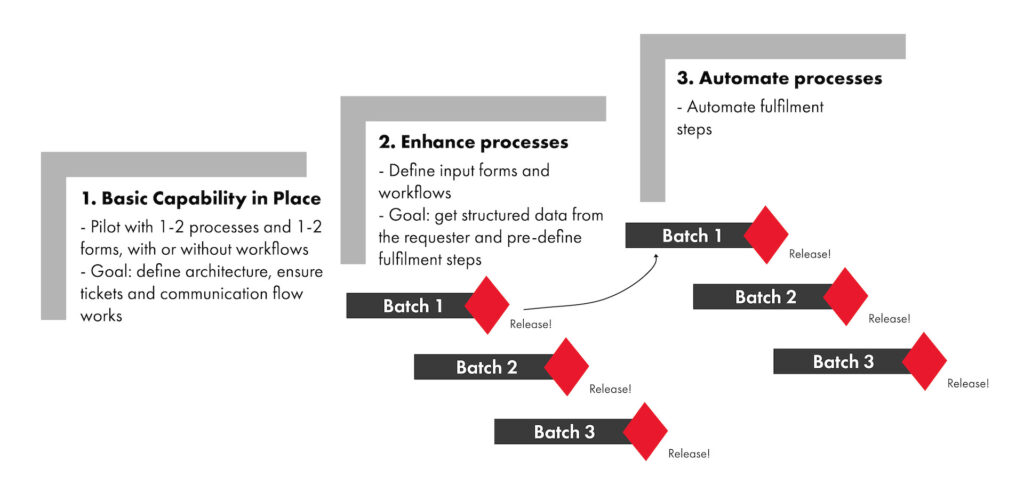
Step 1: Ensure basic capability is in place. Start implementation with a couple of processes. Define forms, architecture and communication flow with end users and other stakeholder groups. In the ESM world, there might be many more stakeholder groups involved than you’d expect. Collect feedback from both end users and fulfillers, improve architecture and communication flow.
Steps 2 and 3: Enhance and automate processes. Start mass definition of requests but do it in batches. Select a few processes in each batch, define input forms to get structured input, release requests for manual fulfilment. Analyse what can be automated from the current batch, then automate it. Meanwhile, start the second batch of the requests. Repeat.
Offer training, define owners, avoid exceptions, expect delays
Finally, here are some additional tips that may help to run your ESM projects successfully:
- We recommend that key stakeholders from the customer side attend a fundamentals training for the selected tool.
- Each request or process must have an owner, who is an expert in the process and who can handle internal discussion and facilitate governance to make decisions that will affect multiple teams.
- Don’t fill in a lack of process maturity with scripts: try to avoid exceptions in the process and script those exceptions. Make the process the same for all use cases.
- If you are an experienced ITSM tool implementation project manager and planning your first ESM project, plan your project schedule and work estimate. Once you’re done, double your estimation. Even after that, there is a chance of delay. Be sure to communicate this openly to your customer.
If you’re still not sure how to proceed, fear not. Sofigate process experts and project managers will recommend the best model for your project and help you carry it out.
Our experts can help in ESM projects with all the steps: project approach and scope planning, process definition, tool implementation, service design and organisation change management. Whether you are considering starting an ESM project or want to spar around this topic, don’t hesitate to drop us a line. We’re here to help!
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Olga Antonova is a Delivery Manager at Sofigate. Olga and her team specialize in helping IT and telecom service providers. Olga has been working with processes and service management tools for the last 15 years.



